Opportunistic Digital Twin: an Edge Intelligence enabler for Smart City
Aug 18, 2023· ,,,,·
0 min read
,,,,·
0 min read
Claudio Savaglio
Vincenzo Barbuto
Faraz Malik Awan
Roberto Minerva
Noel Crespi
Giancarlo Fortino
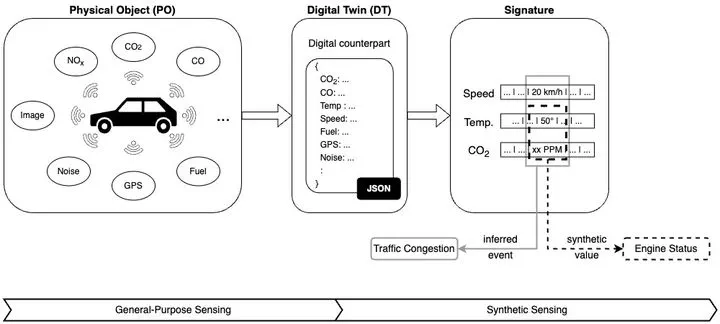 Proposed approach: from the PO (and its DT) to its signature, in which features are “opportunistically” selected and synthetically elaborated
Proposed approach: from the PO (and its DT) to its signature, in which features are “opportunistically” selected and synthetically elaboratedAbstract
Although Digital Twins (DTs) became very popular in industry, nowadays they represent a pre-requisite of many systems across different domains, by taking advantage of the disrupting digital technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Edge Computing and Internet of Things (IoT). In this paper we present our “opportunistic” interpretation, which advances the traditional DT concept and provides a valid support for enabling next-generation solutions in dynamic, distributed and large scale scenarios as smart cities. Indeed, by collecting simple data from the environment and by opportunistically elaborating them through AI techniques directly at the network edge (also referred to as Edge Intelligence), a digital version of a physical object can be built from the bottom up as well as dynamically manipulated and operated in a data-driven manner, thus enabling prompt responses to external stimuli and effective command actuation. To demonstrate the viability of our Opportunistic Digital Twin (ODT) a real use case focused on a traffic prediction task has been incrementally developed and presented, showing improved inference performance and reduced network latency, bandwidth and power consumption.
Type
Publication
ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks